All of the insights I’ve shared thus far have been relegated to optimizing websites for mobile browsers, but there’s another form of user interaction on mobile devices you should be preparing your business for: apps. Apps have surged in popularity, just as mobile devices have, and there’s no sign that their growth has an end point. In fact, they’re responsible for much more mobile use than web browsers.
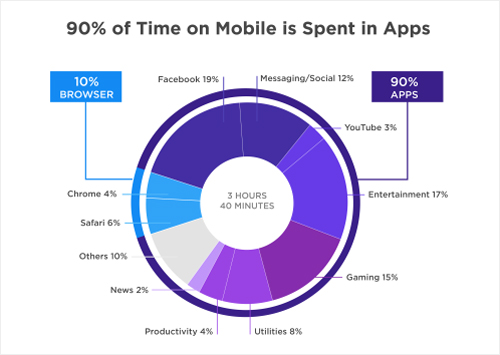
(Image Source: SmartInsights)
To address this, Google’s been implementing a number of functions and updates for what’s becoming known as “app SEO,” including the basic presence of apps in search engines, app deep linking to take users to specific screens within apps downloaded on their devices, and even app streaming, which allows users to access apps they haven’t downloaded.
It’s not entirely certain whether apps may one day replace traditional websites, but they are becoming more important and they’re presenting more opportunities for marketers. Keep a close eye on their development as you fine-tune your strategic approach for mobile users.
Table of Contents
The App Indexing API
Google offers a specific, easy-to-integrate API that will ensure your app is seen and indexed by its search algorithm. However, Android and iOS apps are treated a little differently. Namely, for Android apps, if a user searches for a term specific to your app and has not yet downloaded it, he/she will see it appear in mobile search results. Those who already have the app installed will get Google autocomplete suggestions, along with deep links to content within the app. For iOS, things are a little less beneficial; mobile search visibility only applies for users who have already downloaded the app.
Either way, applying the app indexing API is relatively simple. You can think about it in three steps:
- Make sure HTTP deep links are supported in your app—there are different ways to do this for Android and iOS apps, but I’ll dig a little deeper into that below.
- Directly implement Google’s app indexing API, which they conveniently offer to developers.
- Use rel=alternate link elements or a Schema markup to map various web pages to their app-based counterparts, so Google can gain a better understanding of your app.
That being said, Android and iOS apps do require a bit of a different approach.
Android App Indexing
To get your Android app’s content properly indexed:
- Add intent filters to your manifest so you can dictate how your app will respond to different types of user actions. Action, category, and data tags are the most important. This will allow for HTTP deep links, which is a requirement for app search visibility.
- Use Google’s Search Console to associate your app with your site. This will ensure that Google knows your brand is in control of both your mobile app and your primary domain (and will associate the two).
- Use the app indexing API provided by Google. They give detailed instructions on how to do this correctly.
- Run a test. Fetch as Google to make sure you’ve implemented these steps correctly.
iOS App Indexing
For iOS, the process is a little different:
- Use the “universal links” option to enable HTTP deep link support. If you need help with this step of the process, Google offers a handy guide for developers.
- Use Google’s app SDK to register your app with Google. This will make sure Google recognizes and properly associates your app with an existing website.
- Run a test. Fetch as Google to make sure you’ve implemented these steps correctly.
Apps Without a Corresponding Website
You may have noticed that one of the biggest parts of implementing app indexing is associating an app with a particular website. So what happens if your app has no corresponding website? Unfortunately, do to Google’s current structures and limitations, it is not possible to index your app. However, they are working on developing a new way to index and display app-only content. If you’re interested in being one of the first volunteers for the feature, you can use this form to apply.