Too much of a good thing can be detrimental, especially in SEO.
This is acutely true if you’re not following today’s current “best practices.”
The goal posts are constantly changing. What worked six months ago, may no longer be considered white hat SEO.
Here are fifteen ways a website may be over-optimized, accompanied by tips on how to diagnose and ultimately avoid Google penalty issues stemming from keyword content, SEO advertising circulation, and backlink distribution:
Table of Contents
1. Domain Address Length
Websites with long domain names can over-optimize a site if keywords are part of the address. The best addresses represent brand identity. When adding blogs and other static content, the organic nomenclature of the brand can be integrated as an anchor in a unique address, in place of arbitrary reference. This manages two risks: 1) visitors will be able to locate content externally or in a search; and 2) over-optimization will be null. Here’s a simple example of an exact-match domain over-optimization.

More egregious are those who will take such a domain and then create pages and sub-pages in an attempt to rank (e.g. NewYorkProfessionalPlumbingService.net/Buffalo-New-York-Commercial-Plumbing-Reviews/). If the content is good, it can rank, but better to create a brand and keep both the domain and URL as short as possible.
2. Website Inner Links
Excessive on-page navigation optimization via internal link building or footer links on a single website will inevitably induce over-optimization. While it still serves to have a few pages with standard anchors to map inbound links to a website from external SEO advertising and other marketing collateral, the danger of creating a plethora of inner links is obvious.
3. Duplicate Page Content
The replication of page content (most often referred to as duplicate content) on a single website domain can lead to over-optimization in Google. The When designing a website, text content should be distinct per page. This will assist in reducing search engine crawl and flags leading to penalties. The challenge of course is consistency in brand presence. When adding new news and other content that has a time capsule, avoid repetitious verbatim.
4. Language Syntax
Natural language helps in this case, so as to not introduce duplicate language structure across a single website domain. In sum, cut out the old keyword string to eliminate excess traction. Footer overload and multiple links to content on the site, or to external websites can add dense over-optimization. Select from a limited number of footer links that provide value to the organization or cause.
5. iFrames
Web developers using Javascript and HTML programming of website content often employ iFrames to embed content within a page document. If an iFrame is scripted as a separate object, Google or other search engines imposing penalties for keyword over-optimization will not be triggered by crawling.
6. Multi-media Embeds
The integration of external multi-media content with an embed is a fast and easy method of inserting links and content to a website. If adding a video from YouTube or other widely circulated site, it is always best to embed the code in a secondary page to reduce signals to Google that the value is native to the ‘client’ website’s domain.
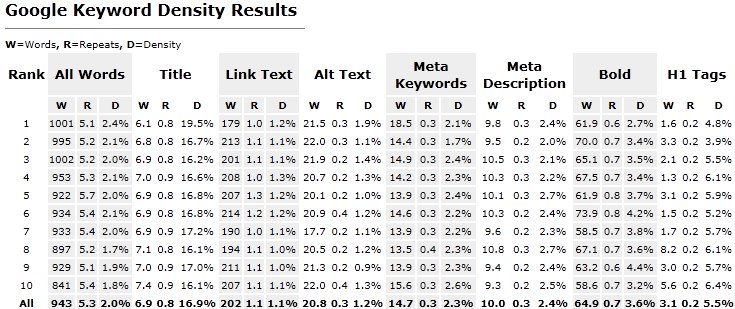
7. Keyword Density
The risk of heavy keyword density on website articles and external content linked to the homepage of a website is relevant enough to review marketing collateral twice before posting to the Internet. Keywords can also create havoc surreptitiously. If a website is part of a link exchange set up for a time capsule relationship and was forgotten about, the former backlink to a domain can generate negative search results.
The density of your keywords matters and here are the rankings stats to prove it:
8. Keyword Misplacement
Google Ads has instituted automatic keyword recognition, which is why SEO and parent sites are ranked according to organic content. Now that everything is indigenous, the rest is up to marketing professionals to follow the new format. Simply rely on title keywords, and add H tags to subtitles to expand the value of collateral. Good content counts, and not against a domain. Loosen up, and write freestyle.
9. SEO Harvesting & Content Syndication
The fact that advertising can now work against top-level, first page visibility, makes it imperative to evaluate old SEO ads that may be linger on the Web. Too many ad posts will generate negative results. Designate content according to online marketing channels to reduce aggregation. This is especially important for advertisers posting across Facebook’s multi-channel ad infrastructure.
Syndicating content can be a great means of increasing exposure, but doing so without marking certain posts as canonical may cause the algo red flags to hit you.
10. Social Media Under-optimization
Social media profiles also provide a relatively standalone approach to retention of the benefits of search engine optimization. The fact that social media profiles are subject to internal search abduction makes it safer to post news and other marketing activity in social media, rather than on a website. Internal search results are always top level within social media, making it less likely that external content will be clicked on. With only one integral link to a social media profile on the homepage of a website, customers, fans, and followers can be seduced without extensive penalties.
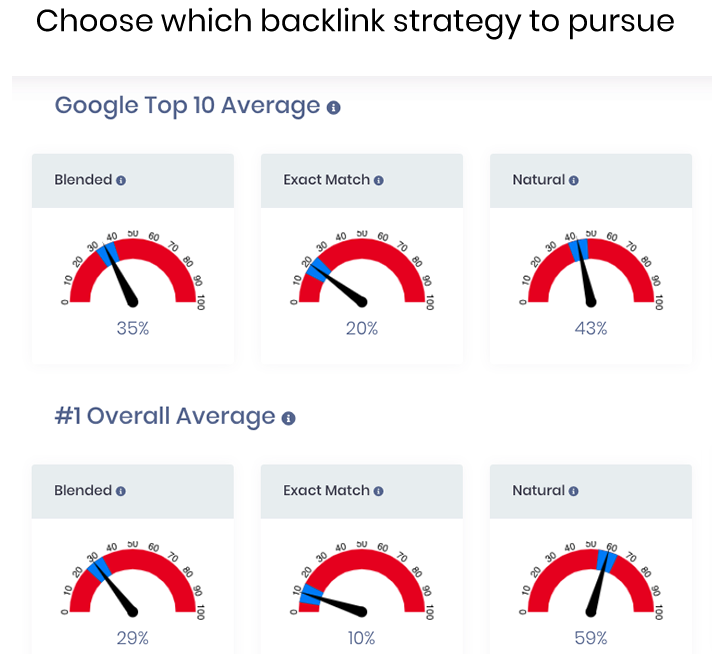
11. Anchor Text Over-optimization
Linking to the aforementioned example site with the phrase “New York professional plumbing service” over and over is one of the most recognized forms of over-optimization. Panda and Penguin Google updates (and subsequent) ensured the algorithm would only rank sites whose anchor te
The percentage variation of your anchor text matters for SEO. For more information, please visit our complete guide on anchor text optimization.
Here are some great rules of thumb for anchor text optimization ratios:
In addition, SEOJet also has a great piece on this very subject (and software that provides visibility to anchor text optimization).
12. Volume Link building
Apps are over-optimizers when supporting text generation activities on an e-Commerce site. Some Web-based apps networks can create hundreds or even thousands of new links per week. The two Vs, velocity and volume are the key. If it appears that a website is suffering from app linking overload, call it quits. This is where our natural link building service comes into play. We take into account diversity, volume, domain authority and link velocity with our client link building.
13. Affiliated Link Exchange
Threads can unravel the entire fabric of website integrity. Mass link exchanges contain an entire roadmap of arbitrary links. Great for sourcing connections, not so productive in an over-optimization scenario.
14. Malicious Backlinks
Toxic backlinks includes links set up by competitors without a website’s owner. SEO harvesting of a site can literally kill it. The mass circulation of search engine optimized ads on the Web can induce another penalty every time a spot is clicked.
15. Content Over-optimization
Some topics might require 10K+ words to rank, while others may rank in the top 3 positions with <500 words. It really depends.
Some would try to convince you that the longer the content, the better.
But content for contents’ sake is foolish. If you can answer the user query in a short blurb, Google may rank you. Sometimes, longer is not always better in SEO.
In an attempt to rank, many websites went out and assumed power pages and pillar content work the ideal in EVERY scenario, which is certainly not the case.
Also, if you’re looking to insert LSI (latent semantic indexing) and entity kewords into your content using something like Cora by SEOToolLab or SurferSEO, you should do so with care. You can go too far in over optimizing your content using SurferSEO and Cora to the point that it hurts your SEO rankings.
In short, you can easily over optimize for length on your landing pages, create an over-abundance of fluff blog posts or create too many location-based landing pages. Take a look at what ranks in the top 20. If the existing sites have an average of 2,500 words and your content has 10K words and a great link profile, you may want to consider trimming the fat. While the length of your blog post matters for SEO, there is definitely a heavy and quickly decrease in marginal returns when it comes to the total number of words you should target.
Preparing for Domain Over-Optimization Triage
If it has been determined that a website is over-optimized the next step is to control for future penalty risk by conducting comprehensive triage on the domain. Prior to establishing the parameters to a new marketing campaign, testing of potential backlinks and other causes leading to Google penalties for ensures that time invested is not wasted.
After a website has been evaluated for penalty causing over-optimization channel marketing magic can renew a site once again. The best link building strategy adds to content marketing value rather than subtract from website performance. Once a marketing strategy goes live, continuous monitoring of performance is important to eliminate the risk of future over-optimization.
Conclusion
Gauging whether your site is properly optimized is best done with testing. If you think your incoming anchor text variation on a particular post is over-optimized, it may be wise to source a few more natural links at a reasonable cost to spread it out.
If you suspect your blog post is too long, spend some time trimming it done, republish it and test the results on that page after a few weeks.
As you test, you will find your performance will improve as you seek improvement!
We also suggest a complete website audit, including a backlink audit so you can flesh out any issues your site may have when it comes to ranking for your desired keywords.
Tim holds expertise in building and scaling sales operations, helping companies increase revenue efficiency and drive growth from websites and sales teams.
When he's not working, Tim enjoys playing a few rounds of disc golf, running, and spending time with his wife and family on the beach...preferably in Hawaii.
Over the years he's written for publications like Forbes, Entrepreneur, Marketing Land, Search Engine Journal, ReadWrite and other highly respected online publications. Connect with Tim on Linkedin & Twitter.
- How to Rank for Local SEO in Multiple Locations - April 16, 2024
- SEO for Mass Tort Lawyers: Everything You Need to Know - April 3, 2024
- Natural Backlinks vs. Unnatural Backlinks: How to Build a Natural Link Profile - April 1, 2024